
BRIEF HISTORY
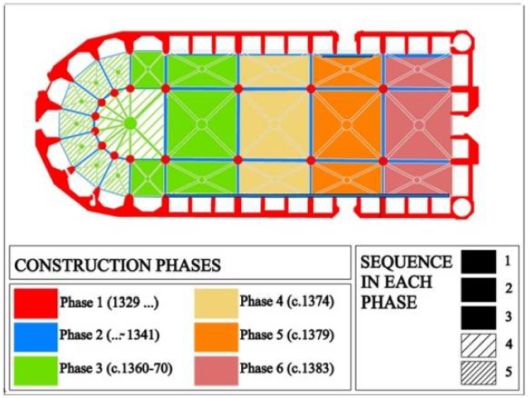
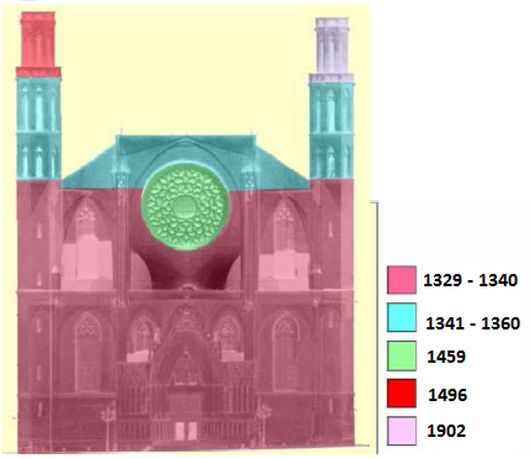
Santa Maria del Mar was built just in 54 years, from 1329 to 1383. According to historical evidences, the church was partially working even before 1350. The majority of the lateral chapels were already built between 1339 and 1352, and then the head chapels were built between 1360 and 1370. During the construction of the vaults, a temporary wooden roof supported on the transverse arches was covering the place making it functional. The current towers were built in 1496 and 1902.
The church has suffered over and over from basically two types of destructive events: earthquakes and fires.
The first earthquake in 1373 occurred during the construction and it provoked the collapse of part of the eastern tower. But it was reconstructed immediately afterwards.
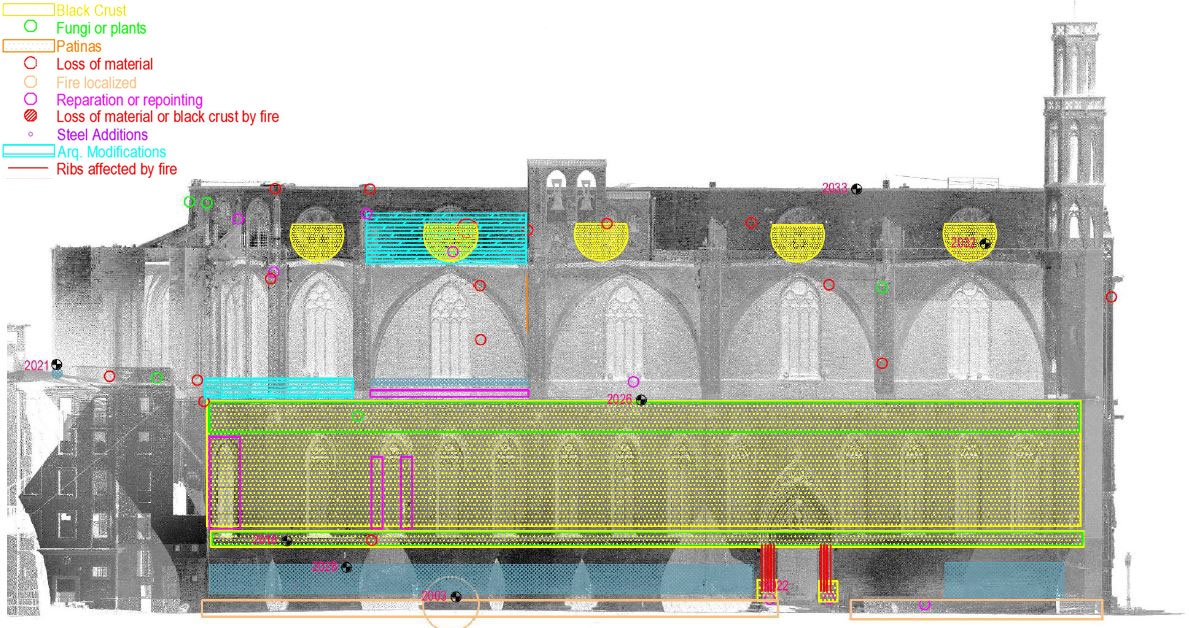
In 1379 there was a fire that affected almost the entire church and mostly damaged the vault of the second section. The following year those damages were repaired.
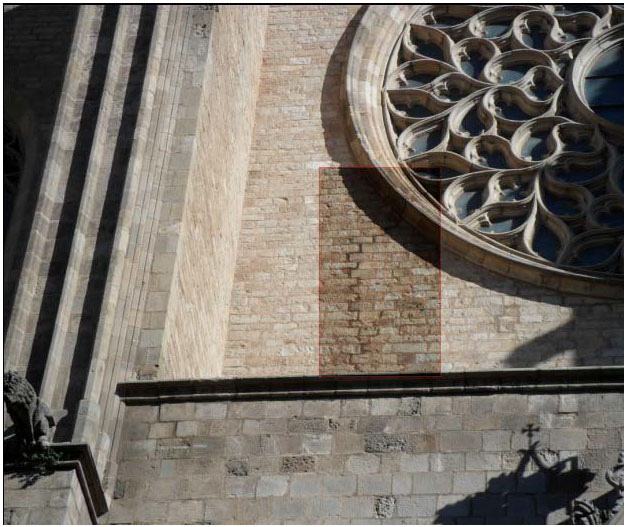
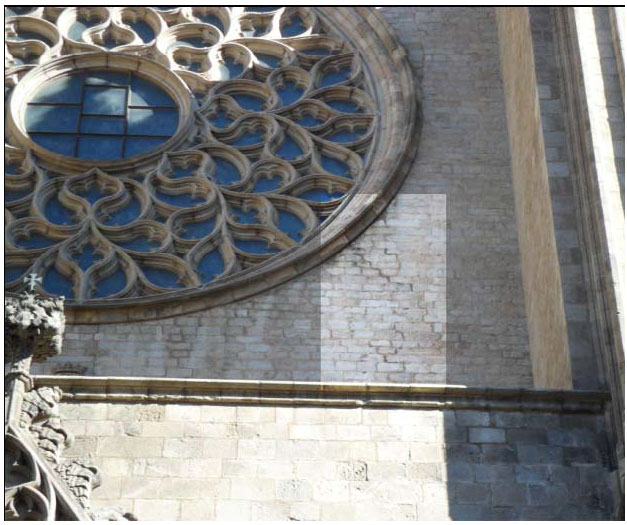
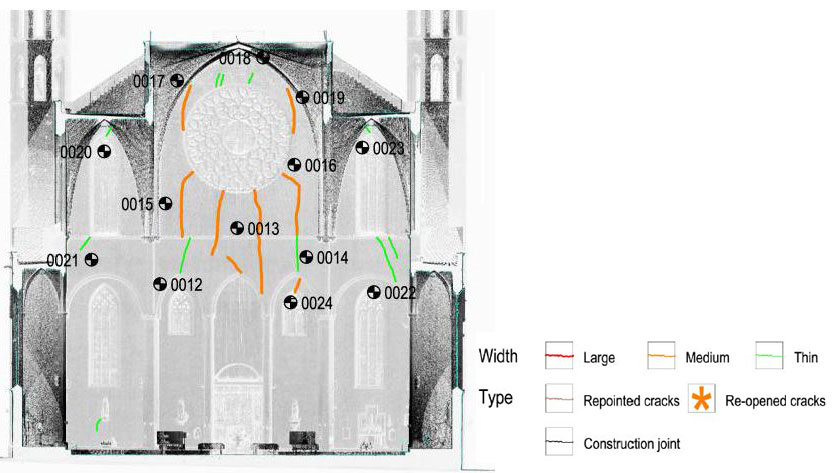
In 1428, another earthquake happened. It caused the fall of the rose window killing 20 people, as well as some damage on the facade. Although, the facade was restored in 1459.
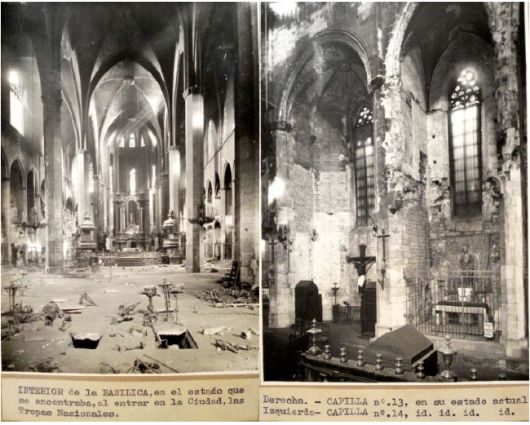
The fire of 1936 during the Spanish Civil War affected mostly the old presbytery and the altar. The fire revealed part of the damage caused by the fire in 1379 as well. These damages are confirmed through the photographic survey.






















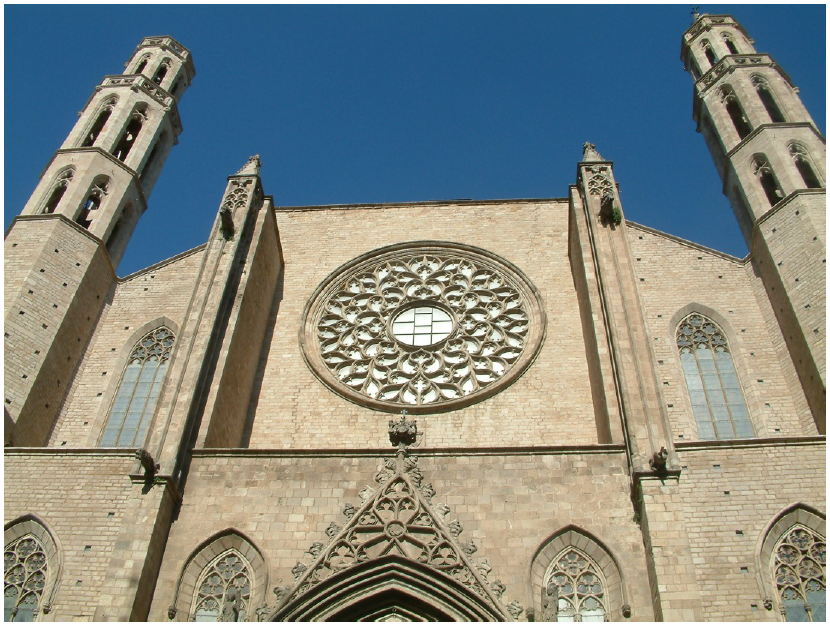
ARCHITECTURAL FEATURES AND GEOMETRY
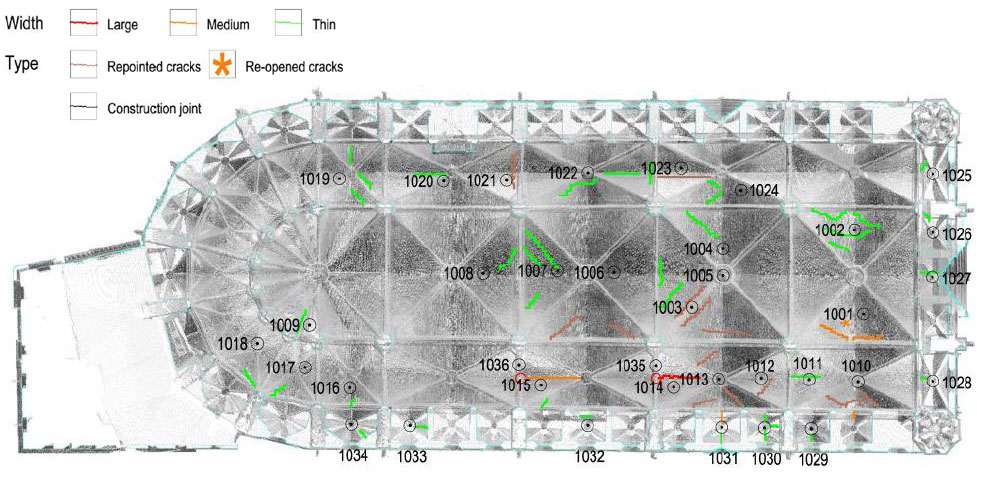
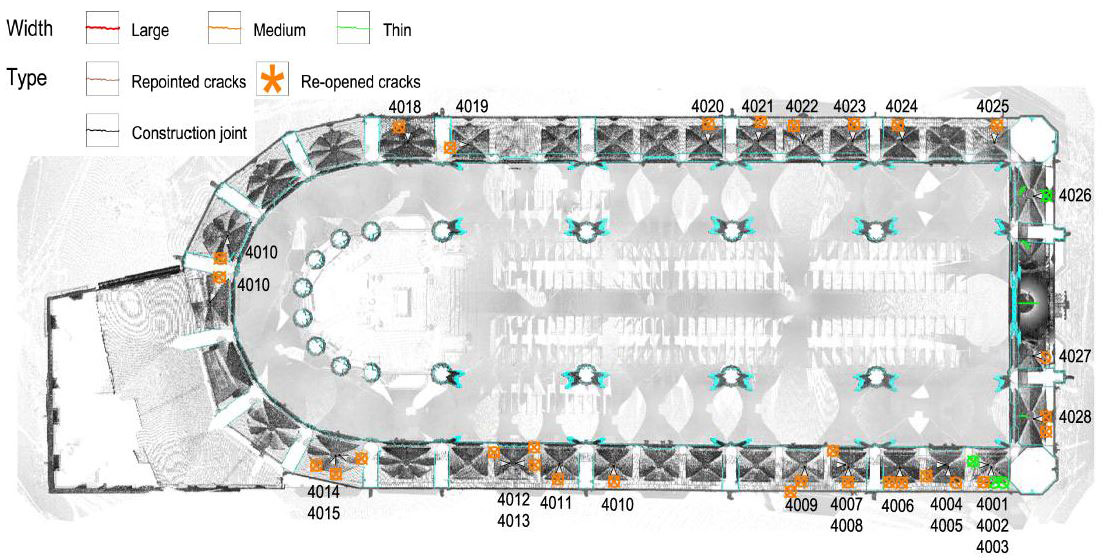
The building is made up of three naves with four sections and an altar surrounded by seven chapels with cross-vaults. The total width is 35.30 m and the length 85 m. The top height of the central-nave vault is 32 m. The octagonal piers are 26 m high and the span is 13 m long. Each central section has 13x13 m2 square cross vaults. The height of the lateral vaults is 26 m and hence, it is said to be relatively high considering that they are lateral chapels.
There are two towers in the facade: the eastern tower is 46 m high and the western one is 47 m high. The diameter of the rose window is about 9 m.
The buttresses are 14 m high from the roof of the chapel to the top of the buttress. Some of the buttresses are 1.5 m wide and others 1.38 m. The vaults are built of about 20 cm thick brick. In the central vault the infill is composed of ceramic pieces and the thickness is around 0.7 to 1 m.
The masonry is mainly constituted by Montjuïc stone and lime mortar. Its mechanical properties were characterized in previous studies and are the following: specific weight = 22 KN/m3; compressible strength = 30 MPa; and the elastic modulus = 10 GPa.
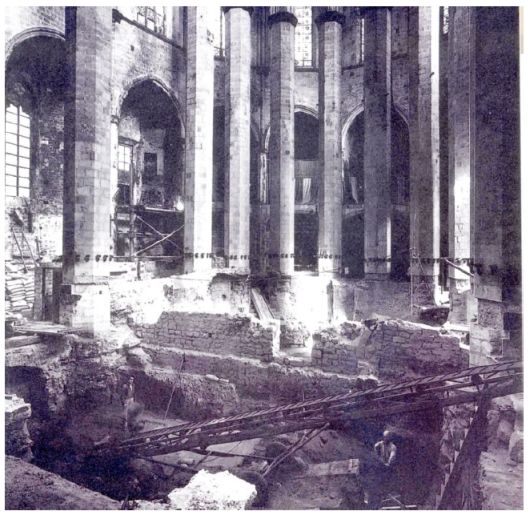
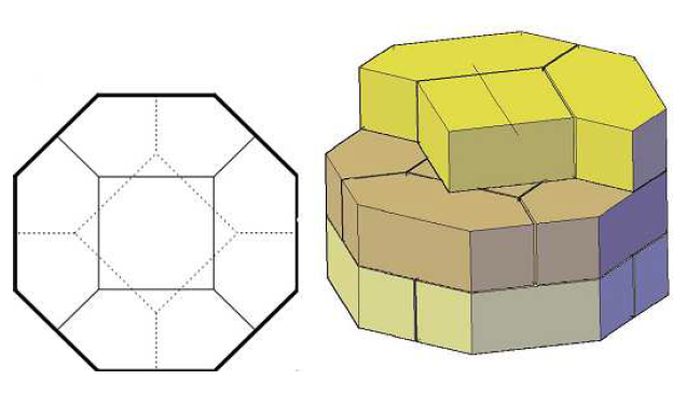
Concerning the piers, there is a squared stone in the center, surrounded by four hexagonal stones, forming an octagonal shape. This represents one unit, and each unit is positioned rotating 45 degrees from the lower unit, in order to ensure stability. The higher stiffness and strength of the piers when compared with the other elements of the structure confirm their essential role in the global behavior of the structure. Their height is 26 m and the diameter around 1.5 m.
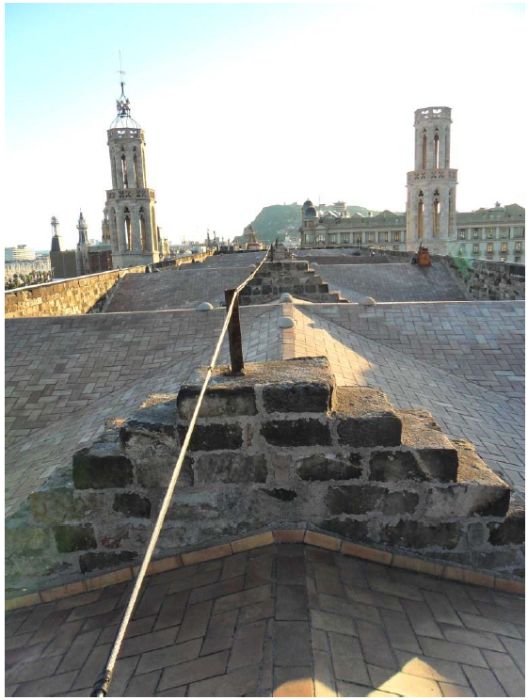
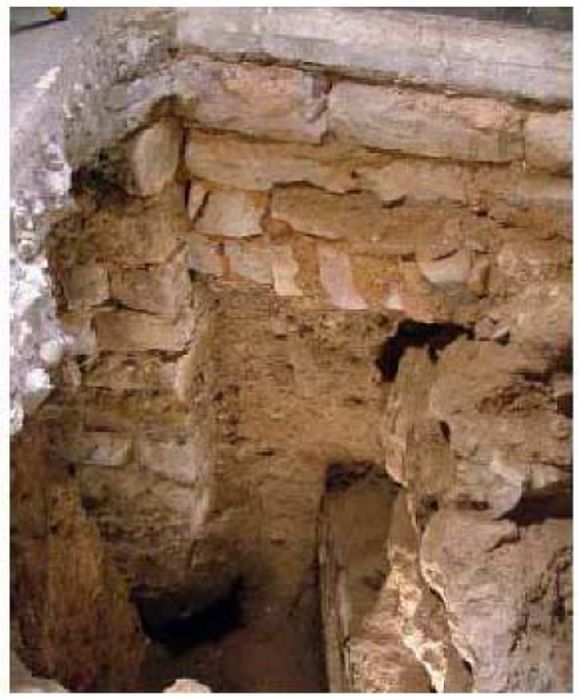
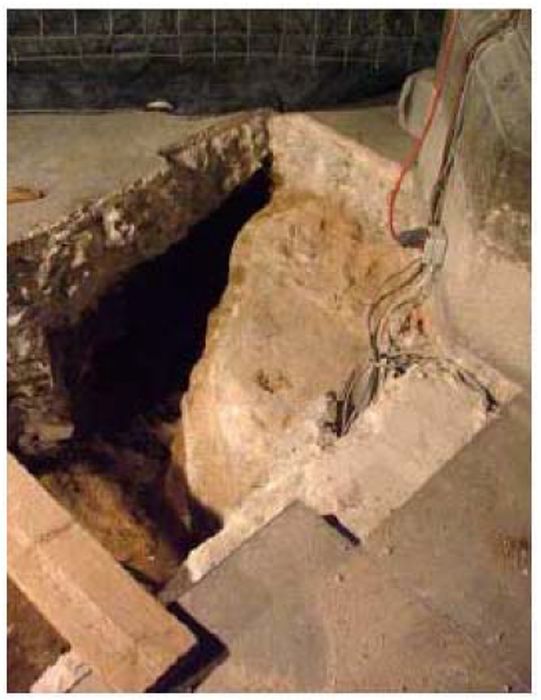


















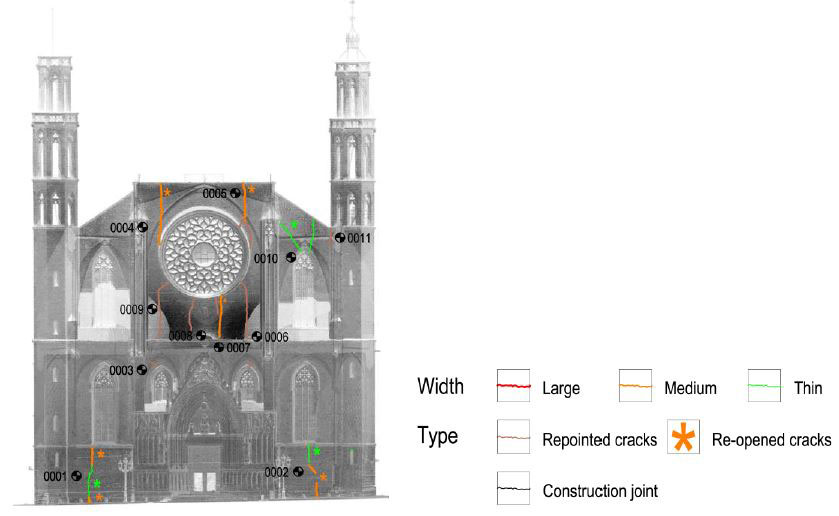
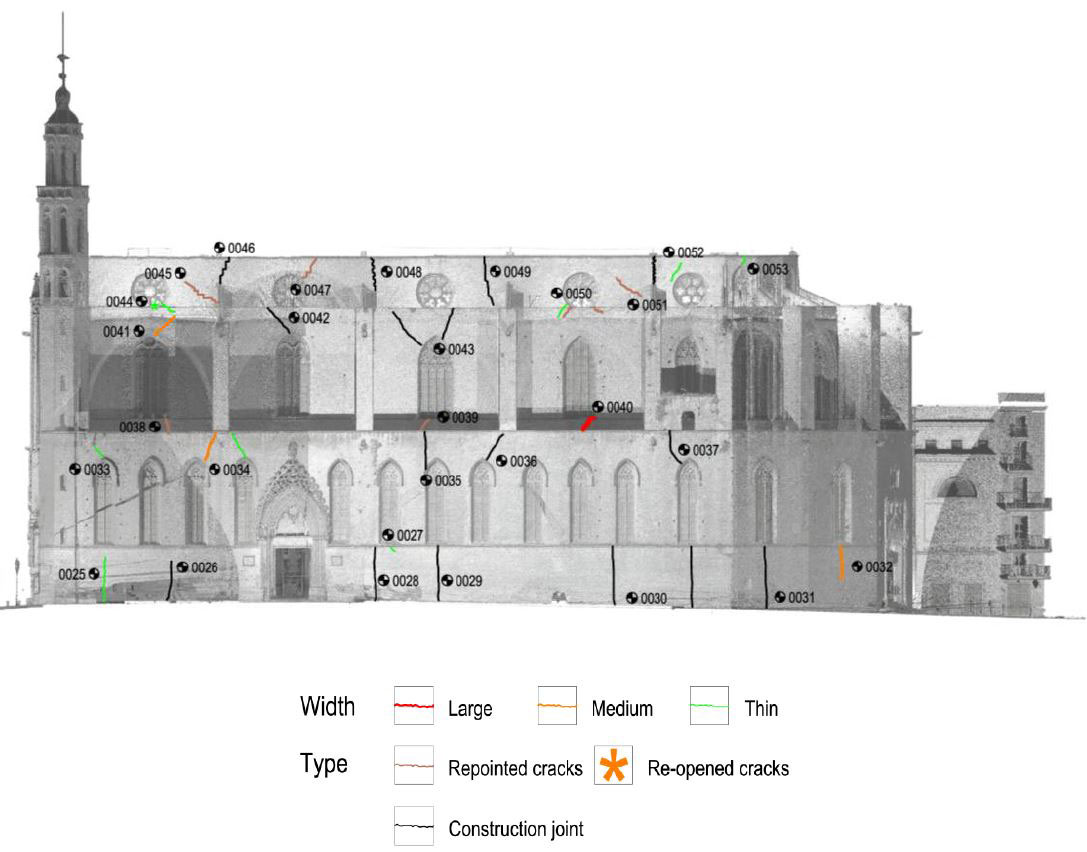
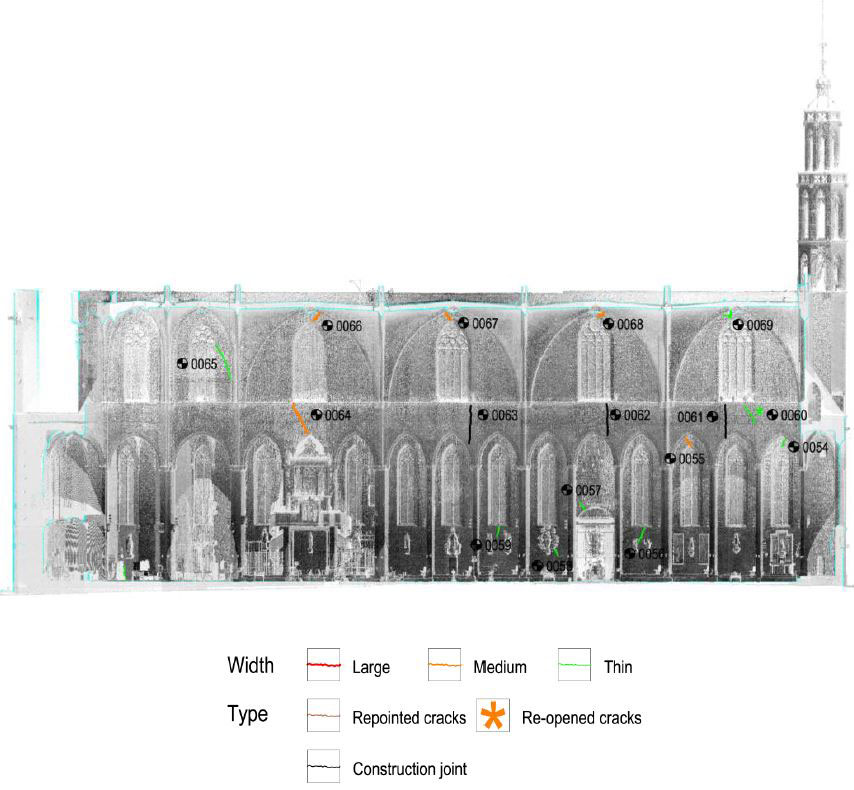
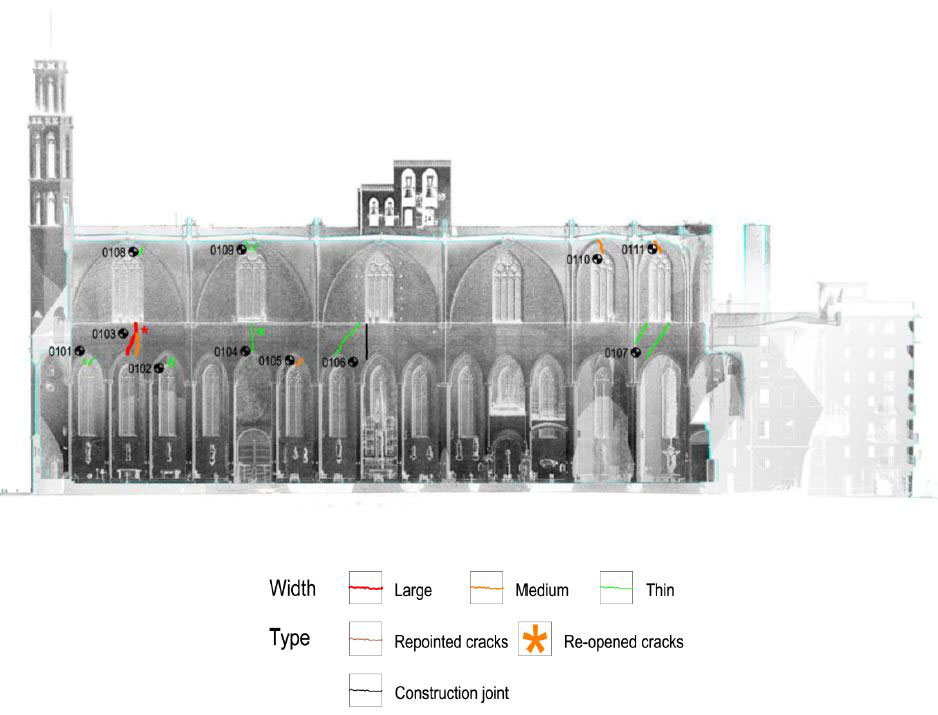
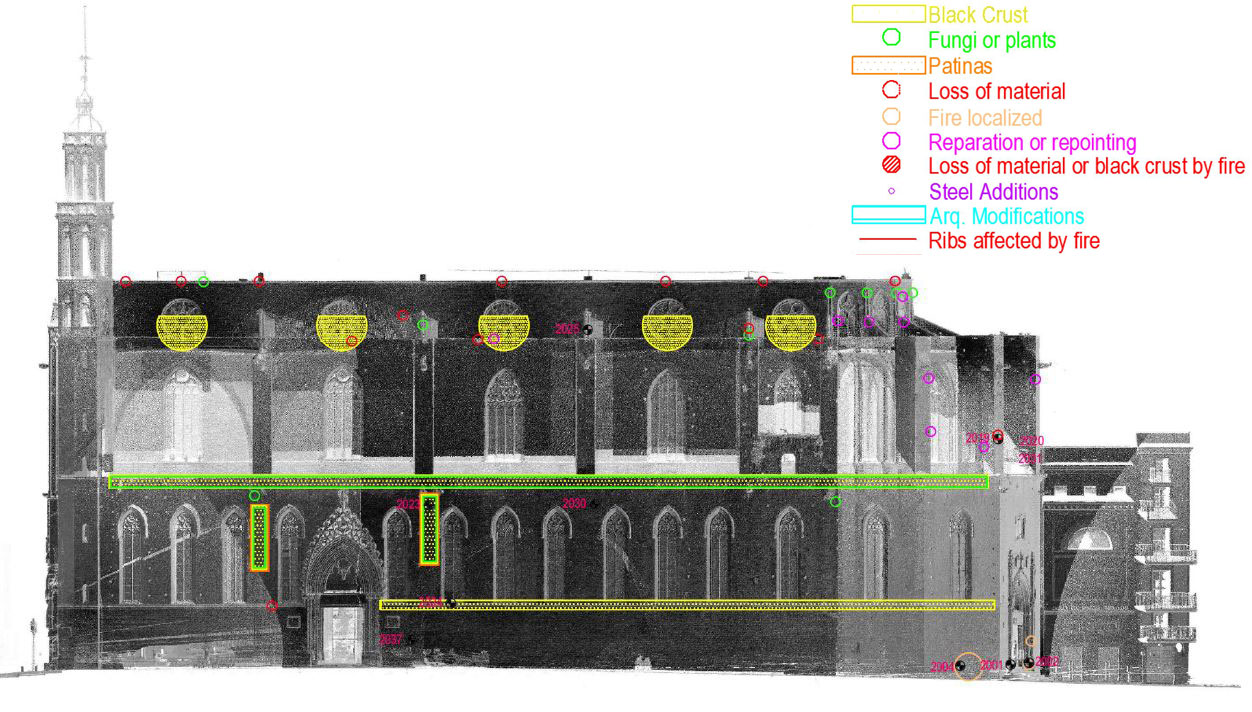
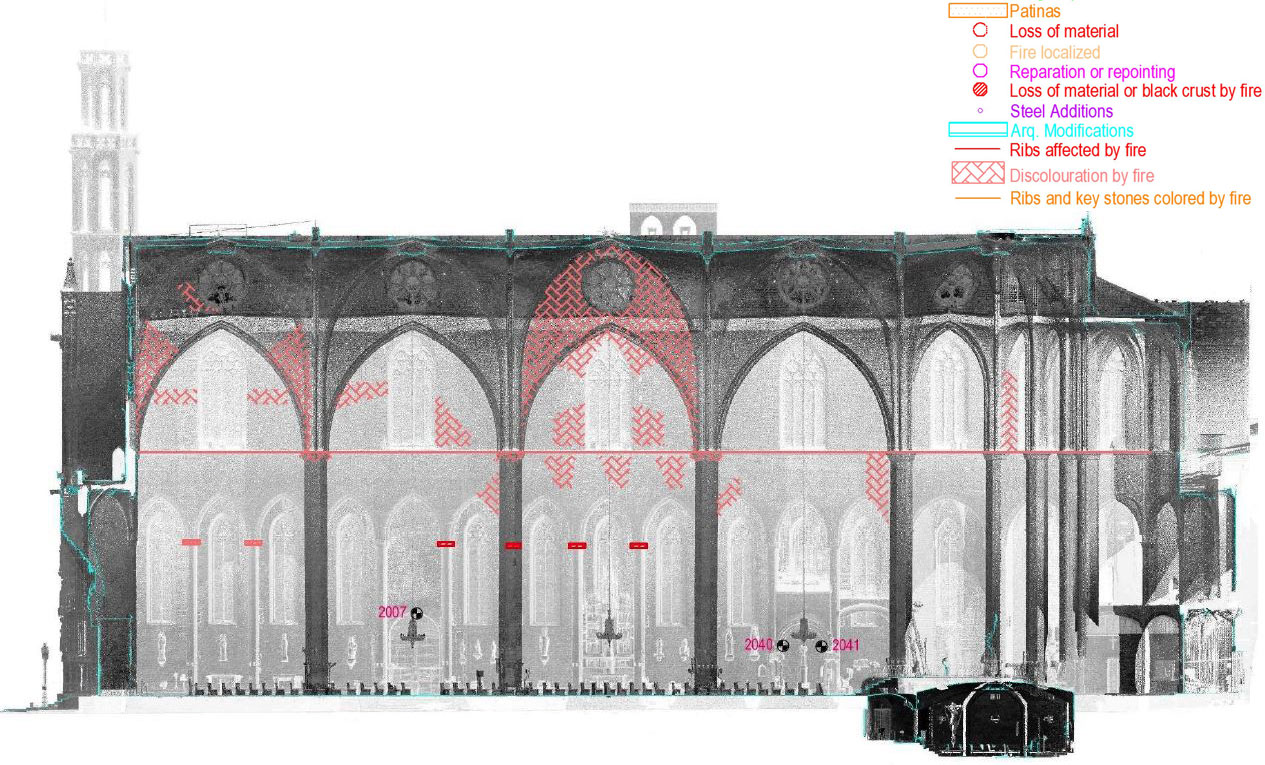
DAMAGES AND DIAGNOSIS
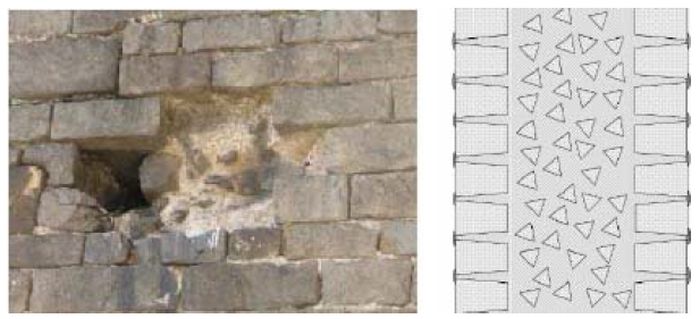
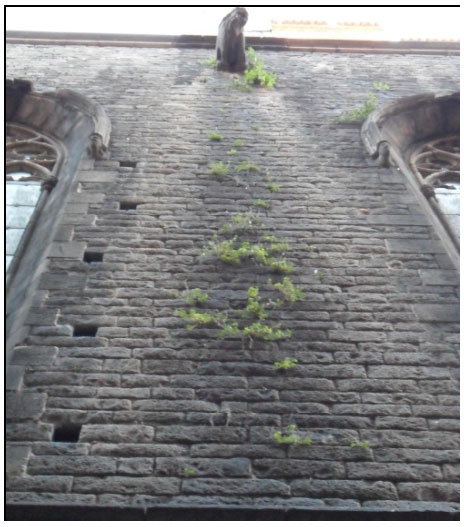
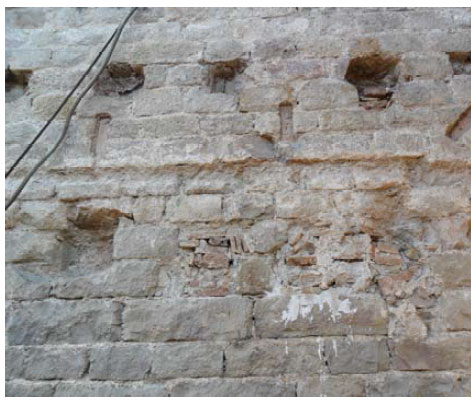
The piers are the most damaged structure. Some of them show an important loss of material (mortar and stone) and others show splitting of the material in the corners. This could have also been caused by a high compressible stress concentration but the most probable it was due to the fire.
The interior of the church shows the presence of different colors due to fire. The most obvious is the black discoloration, but other pink and brown parts are also present on the vaults of the naves.
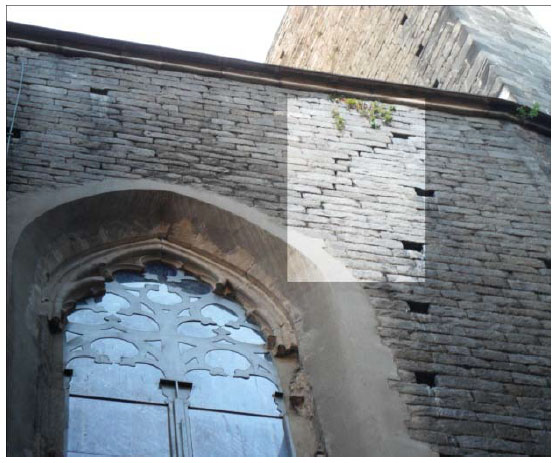
































REFERENCES
[1] P. Roca Fabretat, “Study of Gothic churches: inspection, monitoring and structural analysis,” in III Jornadas Técnicas Internacionales de Tecnologia de la Rehabilitación y Gestión del Patrimonio Construido : REHABEND 2009, 2009, pp. 1–19.
[2] J. Sales-Carbonell, “Santa María de las Arenas, Santa María del Mar y el anfiteatro romano de Barcelona,” Rev. d’Arqueologia Ponent, vol. 21, pp. 61–73, 2011.
[3] P. Roca Fabregat, A. Vacas Albalà, R. Cuzzilla, J. Murcia Delso, and A. Das, “Estudi del comportament sísmic de l’estructura de Santa Maria del Mar, Santa Maria del Pi i la Catedral de Mallorca,” in 2a Trobada de les Egipcíaques: el gòtic meridional català: cases, esglésies i palaus, 2008, pp. 187–203.
[4] P. Roca Fabregat, “Construction Process, Damage and Structural Analysis. Two Case Studies,” in Sixth Interantional Conference on Structural Analysis of Historic Construction, 2008.
[5] P. Giráldez, M. Vendrell Saz, F. Gaballé, R. Pero, and P. Roca Fabregat, “La Basílica de Santa Maria del Mar de Barcelona. Estudi històrico-constructiu, materials de construcció i estabilitat estructural,” Barce.
[6] A. Millán Gómez, Santa Maria del Mar in its context. Edicions UPC, 2003.
[7] P. Roca Fabretat, A. Vacas Albalà, R. Cuzzilla, J. Murcia-Delso, and A. Das, “Estudi del comportament sísmic de l’estructura de Santa Maria del Mar,” in 2a Trobada de les Egipcíaques: el gòtic meridional català: cases, esglésies i palaus, 2008, pp. 187–203.
[8] P. Albacinar, “Damage survey and collapse mechanisms due to seismicty in Gothic Churches around Catalonia region and Mallorca,” Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2010.
[9] J. Murcia Delso, “Seismic analysis of Santa Maria del Mar church in Barcelona,” Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2008.
